Castellated and cellular beams are structural steel beams with web openings that significantly enhance structural efficiency, aesthetics, and functional utility. This design approach allows for greater spans with lighter weight sections, providing a balance of performance and cost-effectiveness in steel construction.

History and Development of Castellated and Cellular Beams
The concept of web openings in steel beams has been around since the early 20th century. Castellated beams, characterized by their hexagonal openings, and cellular beams, with circular openings, were initially used in Europe, driven by a need to optimize steel use. In the 1940s, as automation improved and architects sought more efficient design methods, the use of castellated and cellular beams saw a resurgence. These beams allow for the accommodation of utilities and enhance the flexibility of structural designs without compromising strength.
Fabrication Process
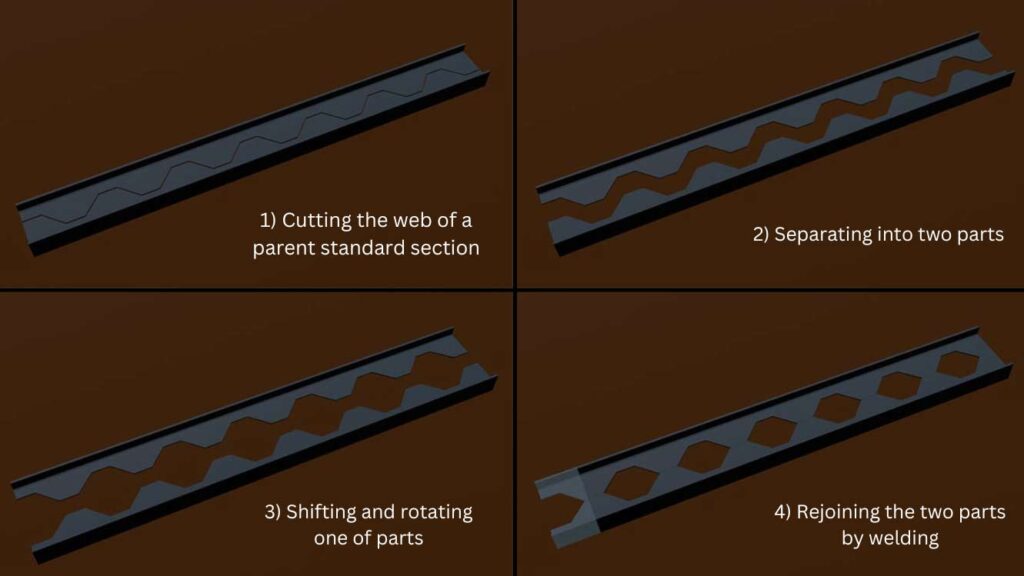
Castellated and cellular beams are custom-designed to fit specific project needs. The process begins with a standard wide-flange beam, which is cut using a precise zigzag or semicircular pattern along its web. For castellated beams, the sections are offset and welded back together to create the characteristic hexagonal openings, while cellular beams are created through a similar method but with circular cuts, requiring two passes of the cutting torch.
Applications and Advantages of Castellated and Cellular Beams
The versatility of castellated and cellular beams makes them suitable for various applications across industries, including parking structures, industrial facilities, and office buildings. These beams are particularly advantageous in long-span construction projects that benefit from reduced material weight, fewer columns, and better space utilization.

- Parking Structures
Castellated and cellular beams are well-suited for parking garages. Their increased depth-to-weight ratio provides the required strength while reducing material costs. The open-web design also allows for better light transmission, making parking structures brighter and more visually appealing.
- Industrial Facilities
In industrial buildings, castellated and cellular beams offer excellent vibration resistance and are ideal for supporting mezzanines, overhead conveyors, and other equipment. These beams minimize the number of required columns, providing more open and flexible workspaces.
- Service and HVAC Integration
One of the primary benefits of these beams is their ability to integrate utilities within their web openings. This feature reduces the building’s overall height and simplifies the installation of HVAC, electrical, and plumbing systems, which can be routed directly through the beams.
- Construction Efficiency
Using castellated and cellular beams reduces the number of structural components required for a project, cutting down on both material costs and construction time. Fewer columns mean fewer foundations, which can lead to substantial savings in both labor and materials. Additionally, these beams allow for quicker construction schedules, which translates to earlier revenue generation for building owners.

Key Structural Benefits
- Improved Aesthetics
Castellated and cellular beams offer architectural appeal, especially in buildings where the beams are exposed. Their unique shape allows for creative design options, including cambered or curved beams that can be fabricated during the manufacturing process. - Vibration Resistance
With their increased depth, castellated and cellular beams are stiffer than traditional wide-flange beams of equivalent weight, providing superior vibration resistance. This makes them ideal for use in buildings where floor vibrations can be a concern, such as hospitals or office spaces. - Cost Efficiency
The long-span capabilities of these beams enable the use of fewer structural components, which can lower overall construction costs. Their ability to carry utilities within the beam’s depth also results in reduced ceiling heights and more efficient space planning. - Flexibility in Design
The ability to custom-manufacture castellated and cellular beams to any depth within a project’s design specifications offers a high degree of flexibility. This adaptability allows engineers to optimize the structural performance of each beam, providing the exact strength needed for specific loading conditions.
Design Considerations
While castellated and cellular beams offer significant advantages, there are also some design complexities to consider. These beams require more detailed analysis due to their unique structure, and engineers must account for additional failure modes, such as web post buckling and shear deformations. The design process involves calculating forces at each web opening and ensuring the beam’s strength in both noncomposite and composite applications.
- Web Opening Size and Spacing
The geometry of the web openings and the spacing between them are critical to the structural integrity of the beam. While the strength of the beam is enhanced by the web openings, engineers must ensure that these openings are appropriately spaced to avoid weakening the structure.
Check out this sample project showcasing a cellular beam design in IDEA StatiCa for insights into advanced structural analysis and design.
- Increased Fabrication Time Required
While cellular and castellated beams offer numerous structural and aesthetic advantages, one primary consideration is the increased fabrication time required. The complex cutting and welding processes involved in creating the distinctive web openings take more time and precision compared to standard beams. For cellular beams, the circular cutting pattern requires two passes, adding additional handling and production steps. Consequently, project timelines may need adjustment to accommodate the longer fabrication process, which can slightly increase costs but often pays off in terms of structural efficiency and flexibility in utility integration.
This increased fabrication time is a trade-off that builders and engineers must weigh against the benefits, particularly when designing for projects that require the open floor plans, light transmission, and utility integration advantages that castellated and cellular beams uniquely provide.
- Special Considerations for Fireproofing and Coating
Fireproofing castellated and cellular beams presents unique challenges due to their open-web design. Intumescent coatings or spray-on fireproofing are commonly used to protect these beams in high-risk environments. Additionally, for outdoor applications or parking structures, an epoxy-based or galvanized coating system is recommended to prevent corrosion.
Conclusion
Castellated and cellular beams provide architects and engineers with the flexibility to design more open, aesthetically pleasing, and cost-effective structures. However, the design of castellated and cellular beams requires careful attention to detail, particularly in terms of web opening geometry, shear forces, and fireproofing considerations.



